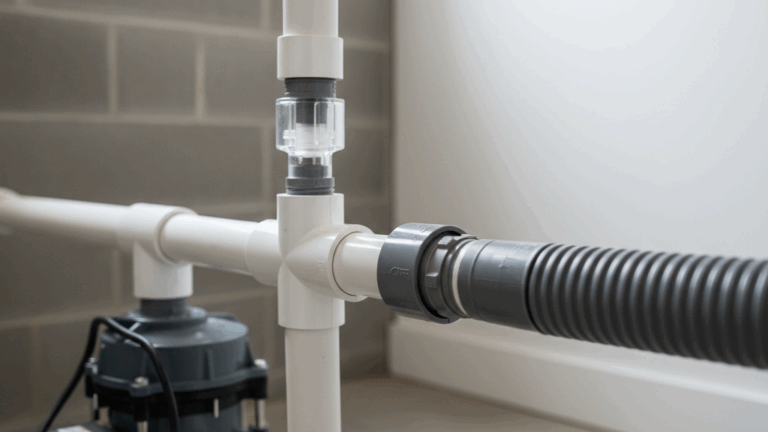
What’s the Difference Between a Sump Pump and an Effluent Pump? Sump Effluent & Sewage Pumps Explained
Understanding the differences between sump pumps, effluent pumps, and sewage pumps is essential for homeowners and property managers looking to protect their homes from water damage and manage wastewater effectively. Each pump type serves a unique function, with specific roles in drainage and waste management systems. Knowing which pump fits your needs can save you time, money, and potential headaches down the line. In this article, we’ll break down the distinctions between sump and effluent pumps, clarify how they work, and provide valuable insights to help you choose the right solution for your property.
Key Highlights
- Sump pumps prevent basement flooding by removing excess water and protecting your home’s foundation from water damage.
- Effluent pumps manage partially treated wastewater, efficiently moving graywater from septic tanks to secondary treatment or dispersal systems.
- Sewage pumps are designed to handle raw sewage and solid waste, ensuring safe, sanitary removal from households with basement bathrooms.
- Choosing the right pump depends on your property’s specific drainage, flood prevention, and wastewater management needs.
- Routine maintenance, guided by a comprehensive checklist, ensures long-term pump reliability and prevents costly water or sewage damage.
Understanding the Roles of Sump Pumps and Effluent Pumps
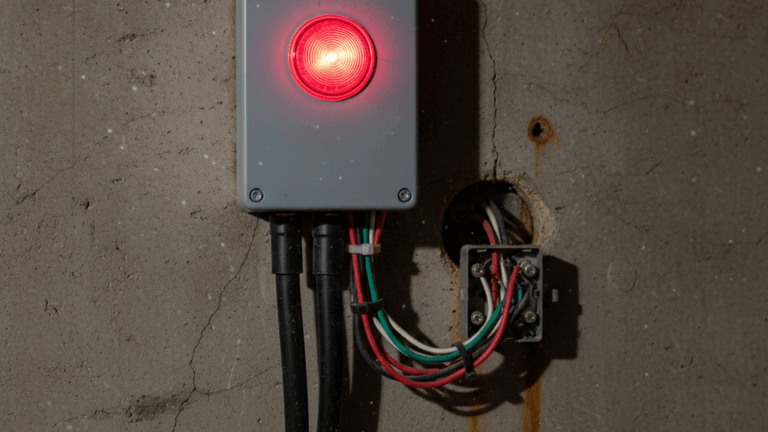
Homeowners often wonder about the key differences between sump pumps and effluent pumps. Both are crucial components of home plumbing, but their roles vary significantly. A sump pump is typically installed in a basin beneath the basement floor, designed to move water away from the foundation and prevent costly damage. Effluent pumps, on the other hand, manage partially treated water that collects in septic or treatment tanks. Each pump uses specific float switches and relies on reliable operation to protect your property. Knowing these distinctions is essential for effective water management and plumbing solutions at home.
How a Sump Pump Protects Your Basement from Water Damage
A sump pump is an invaluable asset when it comes to defending your basement against the risks of unwanted water intrusion. Placed within a dedicated sump basin, these sump pumps are designed to detect rising water levels using float switches, then quickly activate to move water away from your foundation before it can seep through cracks or other vulnerabilities. This immediately reduces the likelihood of mold growth, structural decay, and massive repair bills associated with water damage. In homes with poor soil drainage or in regions prone to heavy rainfall, sump pumps offer peace of mind by acting as an automatic response system whenever water accumulates in the lowest parts of your house. Sump pumps rely on a precise plumbing integration to ensure water is channeled through pipes and released at a safe distance from your home, minimizing any risk of it returning to the area. The pump switch is a critical component; when set correctly, it enables the sump pump to operate only as needed. While routine maintenance is essential, modern sump pumps are built with durability in mind, using corrosion-resistant materials to ensure longevity. Advanced designs also offer multiple float switches for added security, in case one fails during significant rain events. Proactive homeowners frequently choose sump pumps that include backup battery systems or dual pumps for additional reliability. With these measures, you can be confident your sump basin remains dry even if storms cause power outages. Investigating the various pumps’ sump options and understanding how each safeguards your property means you’re not only investing in your home’s safety but also in its long-term value. For more guidance on installation, maintenance, or choosing the ideal pump and float switch system, consider turning to resources like Pump Professionals, which deliver trusted expertise in water removal solutions for modern homes.To help you keep your sump pump in optimal condition, consider these practical maintenance tips:
- Test your sump pump every few months by pouring water into the pit to ensure it activates and drains properly.
- Clean the pump inlet screen regularly to prevent clogs that could block water flow and reduce efficiency.
- Inspect the power cord for wear or damage, ensuring it’s securely plugged into a ground-fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) outlet.
- Check the discharge pipe outdoors to make sure it’s clear of debris, ice, or obstructions.
- Examine the float switch to verify smooth movement without sticking, as this controls the pump’s activation.
- Listen for unusual noises when the pump runs, which could indicate worn parts or loose components.
- Schedule an annual professional inspection for a comprehensive check-up and preventative maintenance. Taking these simple steps will extend your sump pump’s life and help safeguard your home from water damage.
Sump Effluent Management: Key Concepts Explained
Sump effluent management is a crucial bridge between household water control and wastewater processing. As homes rely on both sump pumps and effluent pumps for distinct jobs, understanding sump effluent becomes vital. Sump effluent refers to the water collected in a sump basin that hasn’t yet been fully treated or channeled to a septic system. This overview explores how sump effluent differs from other pumped liquids, highlighting factors like solids handling capability and the unique applications for effluent pumps. The coming content uncovers what sets sump effluent apart and why choosing the right control systems, pump motors, and materials like cast iron matters for reliable performance and long-term protection in septic applications.
What Makes Sump Effluent Different from Other Pumped Liquids?
Sump effluent stands out from other types of liquids managed by pumps due to its origin, composition, and the mechanism required for safe disposal or further treatment. Unlike pure stormwater or clear groundwater, sump effluent typically contains a mix of partially treated wastewater, collected from sinks, laundry, or showers, that ends up in septic systems. It doesn’t usually include raw sewage or large solid particles, but it does pose unique pumping challenges compared to clean water. This is exactly where selecting the right effluent pump with suitable solids handling capability comes into play, as the pump must reliably move sump effluent without clogging or overtaxing the motors. A crucial distinction is the relationship between sump effluent, septic systems, and the broader wastewater management process. While sump pumps focus on moving clear water away from basements, effluent pumps are designed to move partially clarified liquid, or pump effluent, from a septic tank or dosing chamber to a leach field or secondary treatment system. The applications for effluent pumps demand materials like cast iron for durability and superior resistance to corrosion, especially considering that sump effluent can contain various organic matter and chemical residues from daily household use. Effluent pumps are engineered for continuous control over fluctuating liquid levels, often using automatic switches and reliable motors engineered for the rigorous demands of wastewater applications. One of the more important aspects in application-specific pump selection is not just the ability to move liquid, but control over the volume and composition of the sump effluent being managed. Submersible pump technology, often used in effluent pumps, allows for quiet, effective operation directly within the liquid environment, minimizing the risk of exposure and ensuring safer handling of effluent. This differs significantly from general utility pumps and even traditional sewage pumps, which are often built to handle not just effluent but heavy solids as well. Understanding these key contrasts helps inform maintenance and replacement decisions for homeowners looking to protect their property and maintain healthy septic systems. Pumps effluent, when matched to correct applications, preserve system integrity and avoid costly septic backups. When properly installed and controlled, effluent pumps safeguard both the environment and property value by ensuring that wastewater moves efficiently to its next stage of treatment or dispersal. In sum, sump effluent management is more than just removing unwanted water, it’s about tailored pumps, control strategies, and material selection that together protect homes and support overall wastewater management.
Sewage Pumps and Their Role in Household Sewage Removal
While sump and effluent pumps manage water and partially treated wastewater, sewage pumps are engineered to handle raw sewage removal from your household plumbing. The primary difference lies in the ability of a sewage pump, or sewage ejector, to transport solids, including waste flushed from a toilet or drained from a bathroom. These pumps are essential for homes with basement bathrooms or laundry areas situated below the main sewer line, as gravity alone won’t carry sewage upward or horizontally to the municipal sewer or septic tank. A sewage pump is typically housed in a dedicated pit, much like a sump basin, but designed specifically for sewage and featuring a robust motor capable of handling solid debris without becoming clogged.
Sewage ejector pumps activate when sewage from the toilet, bathroom sinks, showers, or laundry enters the pit. The float switch triggers the pump as the sewage level rises, efficiently discharging it through a dedicated pipeline toward your home’s main sewage line or septic system. Unlike effluent pumps, which focus on graywater, sewage pumps are constructed to move bulkier and more challenging waste. They’re often manufactured from heavy-duty, corrosion-resistant materials to endure the corrosive and abrasive nature of sewage, ensuring years of consistent operation. Effective design also reduces odors and minimizes health risks by quickly and securely containing sewage within sealed pits until it’s removed, maintaining sanitary conditions in living spaces.
Homeowners relying on a sewage pump system benefit from its ability to manage sewage generated by daily life, whether from the toilet or other bathroom fixtures, without risking backflow, flooding, or plumbing backups. Multiple sewage pumps can be installed in larger homes or buildings with complex sewer layouts, guaranteeing redundancy and peace of mind. Properly chosen, installed, and maintained, these pumps are a cornerstone of safe and compliant sewage removal. As with sump and effluent pumps, understanding the advantages and differences of sewage pumps helps property owners select appropriate technology and avoid costly emergencies, keeping bathrooms and the entire sewage network running smoothly.
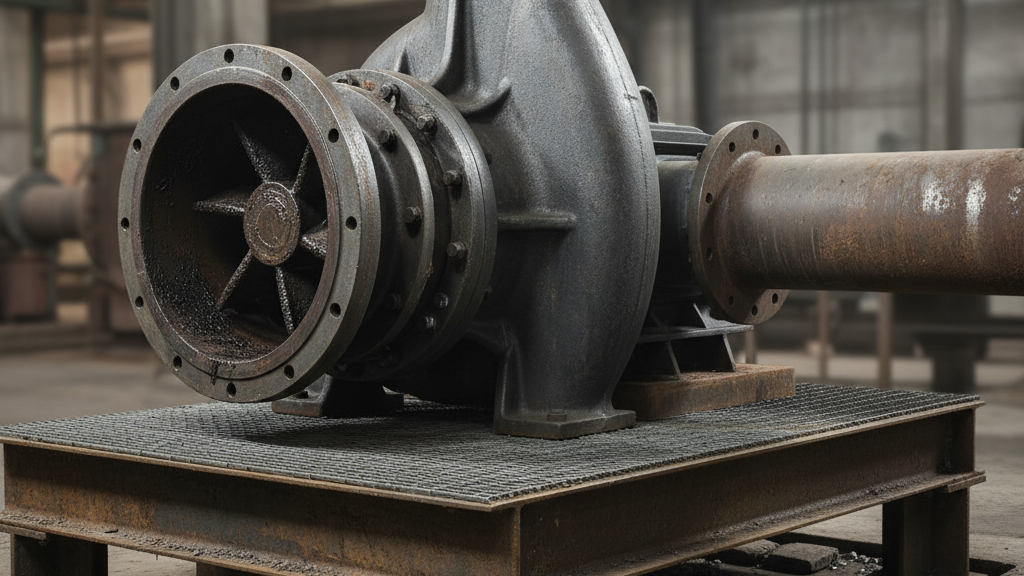

Choosing the Right Pump for Your Property: Practical Tips
Making the right choice between sump pumps, effluent pumps, and sewage pumps depends on the specific plumbing needs and wastewater challenges of your property. Start by identifying your system: homes with basements susceptible to flooding generally benefit from sump pumps, while properties with septic systems require reliable effluent pumps for optimal wastewater management. For properties connected to a septic setup, priorities shift, choosing a pump that can move graywater from the septic tank without clogging or overtaxing the motors is essential for long-lasting performance and environmental protection. Don’t overlook the importance of seamless plumbing integration, especially where control over liquid levels is key to preventing overflows or system failures.
Applications play a huge role in pump selection. For example, if your property produces a high volume of wastewater or contains solids that must move quickly and safely out of the home, consider pumps specifically engineered for these rigorous tasks, like those built for sewage or challenging effluent. Motors should be durable and powerful enough to handle the load. Look for models that come equipped with float switches, allowing for automatic, hands-free operation that responds to rising water or wastewater levels. This not only ensures your pumps activate when needed but also protects against potential overflow, which can compromise plumbing or septic control systems.
Consulting with pump professionals can make a dramatic difference, especially when it comes to matching the right pump to your septic, wastewater, or plumbing applications. For in-depth guidance and a range of trusted products, explore leading manufacturers at Pump Professionals. Their expertise helps property owners select systems offering dependable control and long-term value. Ultimately, the best pump for your property is one tailored to your specific wastewater management requirements, ensuring smooth moves, reliable operation, and lasting protection for your home’s investment.
Downloadable Maintenance Checklist for Sump Pumps and Sewage Pumps
Maintaining your sump pump and sewage pump is the cornerstone of effective water control and flood prevention in any home. Routine attention not only safeguards your property from costly water or sewage damage but also extends the lifespan and performance of your pumps. To simplify proactive care, we offer a comprehensive, downloadable maintenance checklist specifically designed for sump pumps and sewage pumps. This handy resource ensures that nothing gets overlooked, whether you’re monitoring water levels in your basement sump basin or inspecting the power and operation of the dedicated sewage pump in your plumbing system.
Your checklist will walk you through critical monthly, seasonal, and annual tasks. For sump pumps, regular inspection of the float switch is essential; the switch must actuate freely to guarantee that water will trigger pump initiation. It’s just as important to check the discharge line for obstructions, ensuring water flows safely away from your foundation. Cleaning the sump pit and confirming backup battery function help your sump pump system remain reliable during unexpected power interruptions or bouts of heavy rain. Meanwhile, sewage pump maintenance goes a step further: you’ll want to check for debris that might clog the pump inlet, confirm that all electrical connections are secure, and examine seals or gaskets that prevent water or sewage leaks.
Preventive maintenance isn’t just about reliability; it’s about peace of mind, especially with rising water tables or increased wastewater demands in busy households. Mark items as completed on this checklist to ensure you’ve reviewed every critical aspect, from testing your control systems to monitoring the overall condition of your sump pumps and sewage pumps. Download our expert-curated maintenance checklist, and keep your water management and sewage pumps running at peak efficiency year-round. Taking these steps today prevents emergencies tomorrow, because a well-maintained sump pump or sewage pump means a home protected from unwanted water and costly disruptions.
Understanding the distinctions between sump pumps, effluent pumps, and sewage pumps is crucial for selecting the right solution for your home’s drainage and wastewater management needs. By choosing the proper system, you safeguard your property from water damage, ensure efficient waste removal, and maintain a healthy environment. If you’re unsure which pump best fits your situation, consult with a professional to assess your requirements. Investing in the right pump today can prevent costly repairs and provide peace of mind for years to come.
FAQs
What is the main difference between sump pumps, effluent pumps, and sewage pumps?
Sump pumps remove excess water from basements to prevent flooding and protect your home’s foundation. Effluent pumps transfer partially treated graywater from septic tanks to further treatment or dispersal systems. Sewage pumps, or ejector pumps, are designed to handle raw sewage and solid waste, moving it from below-grade bathrooms or laundry areas to the main sewer or septic system.
When should I install a sump pump in my home?
You should install a sump pump if you have a basement that is prone to flooding, poor soil drainage, or live in an area with heavy rainfall. Sump pumps prevent water from accumulating and damaging your foundation, reducing the risks of mold and costly repairs.
How do effluent pumps differ from sewage pumps?
Effluent pumps handle graywater (partially-treated wastewater) without large solids and move it from septic tanks to leach fields or additional treatment. Sewage pumps can handle raw sewage containing solids and are necessary for homes with basement bathrooms or plumbing below the main sewer line.
What maintenance is required for sump and sewage pumps?
Regular maintenance includes:
- Checking float switches for movement
- Cleaning the sump or sewage pit
- Inspecting discharge lines for obstructions
- Testing backup batteries (for sump pumps)
- Examining electrical connections and seals (for sewage pumps). Routine care prevents breakdowns and protects your property from water or sewage damage.
How do I choose the right pump for my property?
Identify your specific needs: if your main concern is basement flooding, a sump pump is best. For septic systems, choose an effluent pump matched to your tank and volume. If you have below-grade bathrooms or laundry that require moving waste upwards, install a sewage pump. Consult a pump professional to assess your requirements and ensure correct installation and compatibility.